Parler
Parler Gab
Gab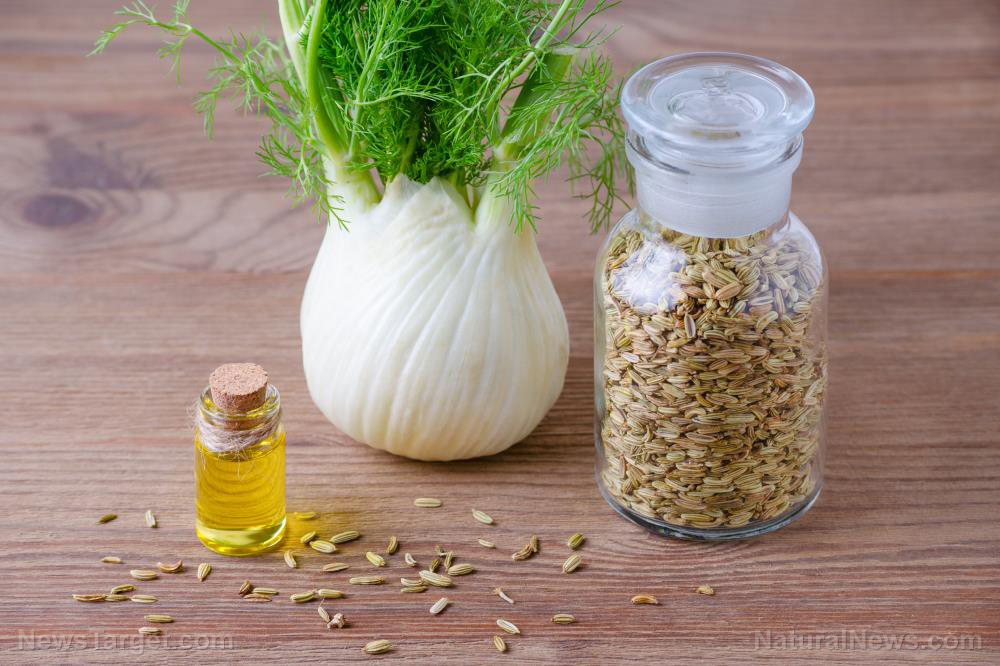
Piper nigrum, commonly known as black pepper, is a highly reputed herb in the traditional Indian medicinal system of Ayurveda. Much of its benefit comes from the component piperine, a bioavailability enhancer and a potential obesity fighter.[ii] Pungent spices like black pepper are also appetite-suppressing.
A 2018 study put this to the test, evaluating whether the consumption of a black pepper-based beverage would affect appetite sensations, postprandial glucose levels, gut hormones, thyroid function and gastrointestinal health after eating a white wheat bread "challenge" meal with 50 grams (g) of carbs.[iii]
In the study involving 16 healthy subjects, the researchers concluded that the black pepper beverage might be beneficial for modulating appetite. According to the study, the beverage modulated appetite by reducing hunger, desire to eat and "prospective consumption," while increasing satiety and fullness.[iv]
2. SpinachA long-term human study from Lund University in Sweden found that a spinach extract containing green leaf membranes known as thylakoids reduced hedonic hunger by up to 95%, as well as increased weight loss at 43%.[v]
Hedonic hunger is the craving that people have for unhealthy foods such as sweets or junk food. In the study, thylakoids reinforced the production of satiety hormones in the body, leading to better appetite control and increased weight loss.
"Our analyses show that having a drink containing thylakoids before breakfast reduces cravings and keeps you feeling more satisfied all day," said Charlotte Erlanson-Albertsson, author and professor at Lund University.[vi]
In an animal study, authors evaluated the appetite-suppressing effect of a flavonoid-rich extract of spinach leaf.[vii] Spinach demonstrated a promising effect by inducing a quicker-than-normal release of cholecystokinin, a short-term satiety signal. This may be due to the high flavonoid content, they added.
3. FennelFennel, which belongs to the Apiaceae family, is an ancient medicinal plant with known antioxidant, anti-inflammatory and antibacterial properties. An animal study on fennel's effect on body weight, feed intake food efficiency rate and serum leptin showed it could reduce the rate of food efficiency -- or the percent of food intake stored as fat -- in the subjects.[viii]
In research among overweight women in South Korea, nine healthy subjects were given fennel tea, fenugreek tea or placebo tea, then provided with a lunch buffet, after which their food consumption was analyzed.[ix] The researchers then measured subjective appetite, hunger, fullness, desire to eat and prospective food intake.
Drinking the fennel and fenugreek teas significantly aided in suppressing subjective appetite among the participants. Compared with placebo, fennel tea translated to less hunger and prospective food intake as well as greater feelings of fullness.foo
4. FlaxseedA food and fiber crop rich in dietary fiber and omega-3 fats, flaxseed is also widely explored for appetite suppression.
In two randomized studies with 24 and 20 subjects each, a small dose of flaxseed fiber substantially suppressed appetite along with energy intake. Administered as drinks or tablets, flaxseed fiber produced similar responses.[x]
In a separate study, four different meals were tested in 18 young men in a double-blind study. Test meals were served after an overnight fast, with flaxseeds in varying forms as the fiber source.[xi] The findings suggested that flaxseed fiber may suppress postprandial lipemia, the rise in blood triglycerides after eating, as well as appetite. Subsequent energy intake, however, was not affected.
5. YogurtA fermented milk product viewed as an essential food and nutrient source, recent clinical evidence suggests yogurt is involved in controlling body weight, therefore helping reduce the risk for Type 2 diabetes.[xii]
Factors at work include yogurt's unique composition, including its lactic acid bacteria, which may affect gut microbiota. Yogurt intake may lead to increased body fat loss, decreased food intake, increased satiety and altered gut hormone response.
"The relative energy and nutrient content and contribution of a standard portion of yogurt to the overall diet suggest that the percentage daily intake of these nutrients largely contributes to nutrient requirements and provides a strong contribution to the regulation of energy metabolism," the authors explained.
Discover more abstracts on appetite-related weight problems on the GreenMedInfo.com database. Read more at: GreenMedInfo.comMike Adams releases music poetry sensation: A Child of God
By Mike Adams // Share
States push back against mRNA injections, announce bans on deadly shots
By Ava Grace // Share
Conspiracy theorists were right about everything – Now what?
By News Editors // Share
Black plum: A nutrient-packed superfood with timeless appeal
By Zoey Sky // Share
Deranged leftists call for violence, assassination of Musk and Trump
By News Editors // Share
Governments continue to obscure COVID-19 vaccine data amid rising concerns over excess deaths
By patricklewis // Share
Tech giant Microsoft backs EXTINCTION with its support of carbon capture programs
By ramontomeydw // Share
Germany to resume arms exports to Israel despite repeated ceasefire violations
By isabelle // Share